Cannabidiol (CBD): Exploring Its Uses, Legality, and Safety
Cannabidiol, or CBD, has garnered widespread attention in media and consumer products, from touted health benefits to everyday items like CBD-infused sports bras. But what exactly is CBD, and why has it gained such popularity?
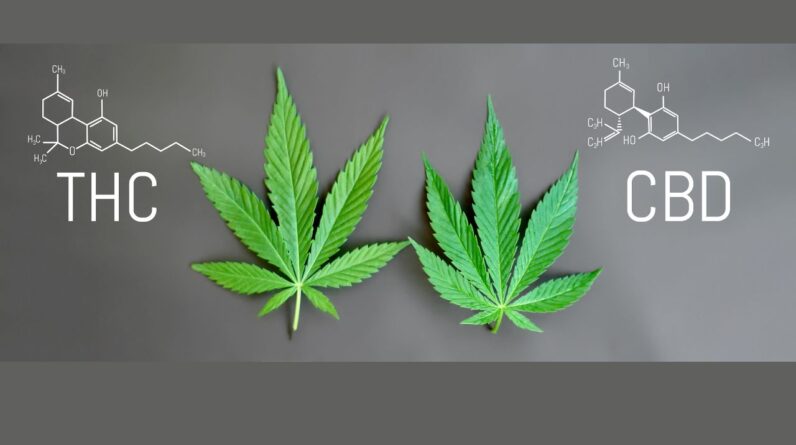
Understanding CBD vs. Marijuana, Cannabis, and Hemp
CBD is a non-intoxicating compound found in cannabis plants, including marijuana and hemp. Unlike tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which produces psychoactive effects, CBD does not cause a “high.” It is extracted from hemp plants, a legal variety of cannabis containing negligible THC levels, or synthesized in a laboratory.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), CBD exhibits no effects indicative of any abuse or dependence potential in humans. It is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, with no evidence of public health-related problems associated with its use.
In the United States, the legal status of CBD has evolved. The 2018 Farm Bill removed hemp and its derivatives from the Controlled Substances Act, legalizing hemp-derived CBD products nationally. However, CBD derived from marijuana remains subject to varying state laws.
The Health Benefits of CBD
CBD has shown the most compelling evidence for treating severe forms of epilepsy, such as Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Epidiolex, a purified CBD oil, is the first FDA-approved cannabis-derived medication for these conditions.
Beyond epilepsy, preliminary research suggests CBD may have therapeutic potential in addressing:
- Anxiety and Depression: Studies in both animals and humans indicate that CBD may reduce anxiety and improve mood by interacting with serotonin receptors in the brain.
- Insomnia: CBD may help improve sleep quality and reduce insomnia by alleviating anxiety and promoting relaxation.
- Chronic Pain: CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties and interactions with neurotransmitters suggest it could relieve chronic pain, including neuropathic pain and pain related to conditions like arthritis.
- Addiction: Some studies suggest CBD may help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms in individuals addicted to substances like opioids, nicotine, and alcohol.
However, more robust clinical trials are needed to conclusively establish these benefits and determine appropriate dosages for different conditions.
Safety Considerations
CBD is generally well-tolerated, but it can cause side effects such as dry mouth, diarrhea, fatigue, and changes in appetite or weight. High doses of CBD may also interact with certain medications by inhibiting liver enzymes responsible for metabolizing drugs, potentially increasing their concentrations in the bloodstream.
Moreover, the lack of FDA regulation for CBD products raises concerns about quality, consistency, and safety. Without standardized manufacturing practices, consumers may be exposed to products with inaccurate CBD levels or contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals, or THC.
To mitigate risks, consumers are advised to purchase CBD products from reputable manufacturers that provide third-party lab testing results (Certificate of Analysis, COA). Consulting with a healthcare provider before using CBD, especially when taking other medications, is crucial to avoid potential interactions.
Forms and Usage
CBD is available in various formulations to suit different preferences and needs:
- Oils and Tinctures: Sublingual administration allows CBD to enter the bloodstream quickly and is often preferred for its precise dosing.
- Capsules and Edibles: These offer a convenient way to ingest CBD, but absorption rates can be slower and less predictable due to digestion.
- Topicals: CBD-infused creams, lotions, and balms are applied directly to the skin for localized relief of pain, inflammation, or skin conditions.
- Vapes: Inhaled CBD enters the bloodstream rapidly through the lungs, providing quick relief but potentially posing risks associated with vaping.
Conclusion
While CBD shows promise as a therapeutic option for various conditions, including epilepsy, anxiety, and chronic pain, its efficacy and safety require further validation through rigorous clinical research. As regulations continue to evolve, consumers should exercise caution, seek reliable information, and consult healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about CBD use.